Tech Disruptors in Education
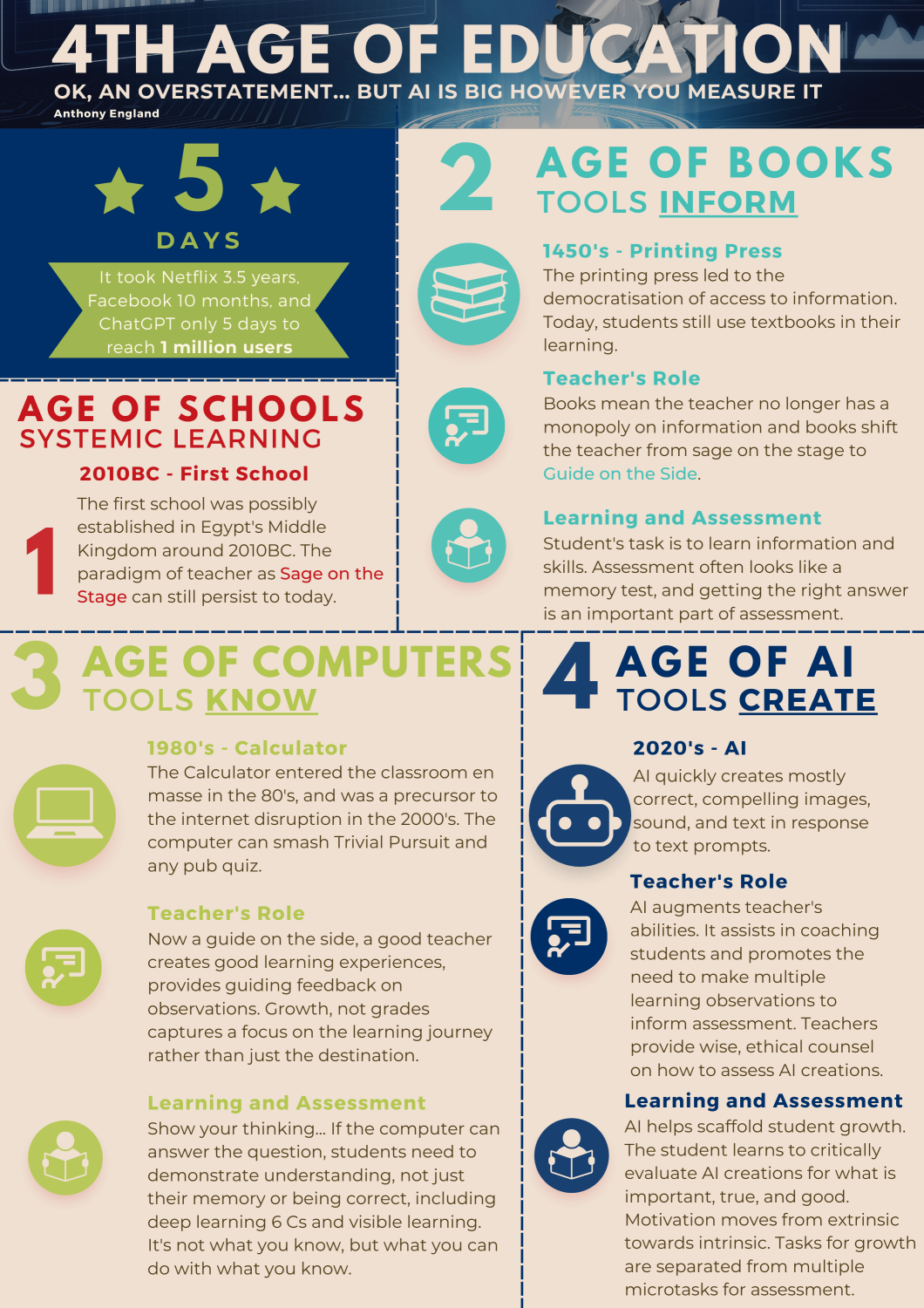
The education sector has undergone significant transformations over the centuries due to technological advancements. These transformations can be categorised into four stages, each representing a shift in the role of educators, students, and the tools used for learning and assessment.
The point of this post is to show we’ve been here before, and hints that tech disruption repeatedly creates a positive shift in what education looks like.
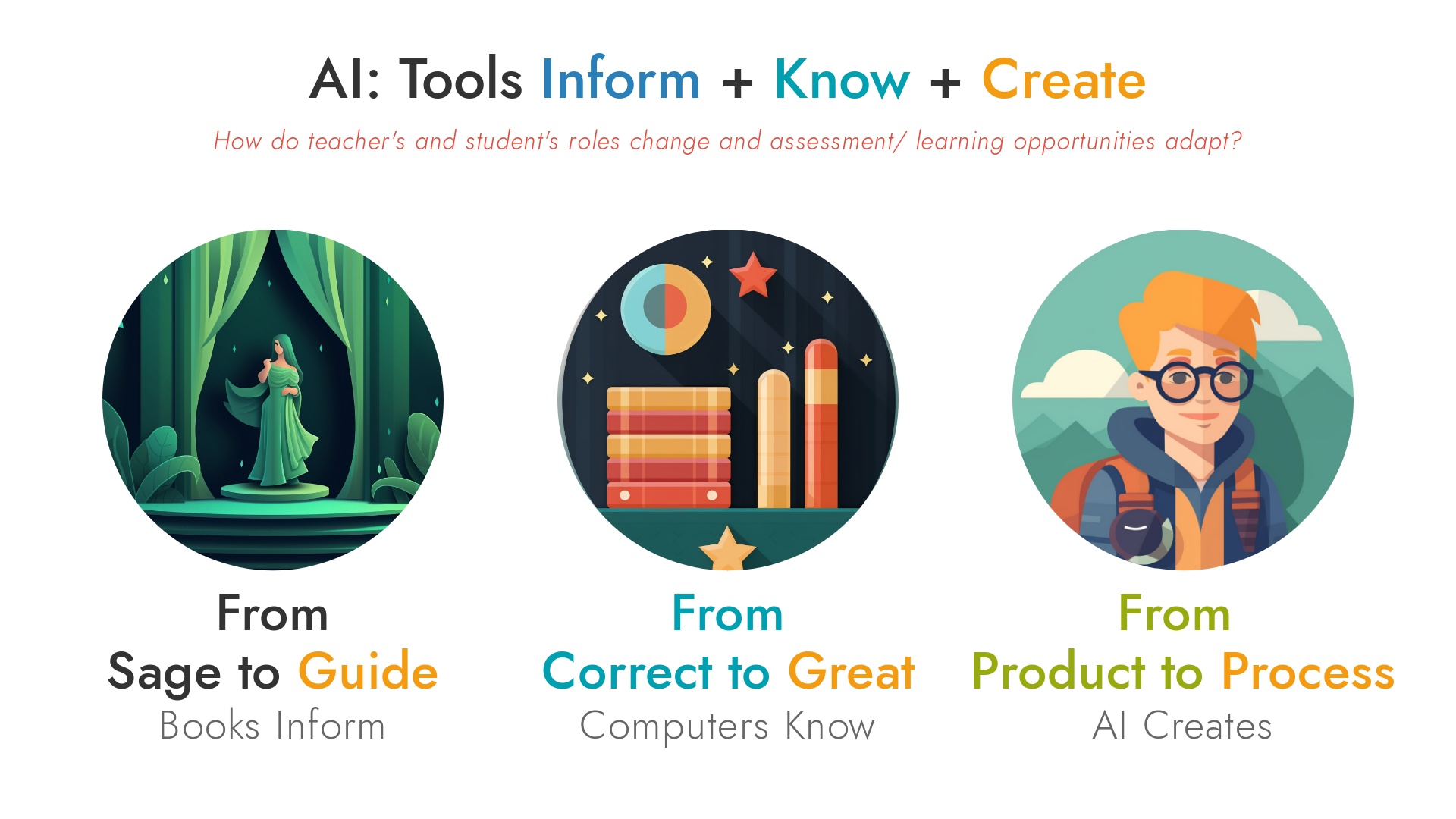
Stage 1: The Sage on the Stage
Education is teacher-centric. Teachers are viewed as the authority and the main source of information. Students rely on oral teachings and are assessed based on their ability to memorise and recall information.
Era: Pre-printing press
Key Technology: None
Role of Teacher: The primary source of information and knowledge.
Role of Student: Passive recipients who record and memorise information.
Assessment: Focus on the ability to recall information.
Stage 2: Guide on the Side
The advent of books democratises access to information. Teachers transition from being the sole source of information to guides who help students navigate and interpret the written material.
Era: Post-printing press
Key Technology: Books
Key Disruption: The tool informs, democratising access to information – effectively removing the teacher as the only source of information.
Role of Teacher: Facilitator guiding students in accessing and understanding information from books.
Role of Student: Active learners who absorb information from books.
Assessment: Understanding and correct interpretation of information from books.
Stage 3: From Correct to Great
With the advent of the internet and calculators, information becomes readily accessible. The focus shifts from memorisation to the application of knowledge. Teachers guide students in developing critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity.
Era: Computer and Internet Age
Key Technology: Calculators, Computers, Internet
Key Disruption: Getting things ‘correct’ is easy – you can simply search for the answer. It’s not just what you know, but what you can do with what you know.
Role of Teacher: Mentor focusing on the development of higher-order thinking skills – ‘6 Cs’ are as important as the ‘3 Rs’
Role of Student: Independent and collaborative learners who apply information to solve problems and create new knowledge.
Assessment: Visible thinking, multimodal demonstration of mastery and quality work produced and application of knowledge.
Stage 4: The Student as Co-Pilot
AI disrupts the education sector by automating content creation and data analysis. Students become co-pilots, actively engaging with AI tools to create content. Students are responsible for assessing the quality of work produced by AI. Teachers collaborate with students, guiding them in critical thinking, ethical considerations, and quality assessment. Assessment becomes more about tracking the process and not just the final product. Student autonomy is elevated.
Era: AI and Automation Age
Key Technology: Artificial Intelligence
Key Disruption: Tools now create. The student is no longer the sole author of work.
Role of Teacher: Collaborator and coach in the learning process. Designing authentic problem-framed learning opportunities that promote student autonomy and empowerment to critically evaluate AI generative content.
Role of Student: Elevated autonomy, co-creators and assessors of work produced by AI.
Assessment: Intrinsically motivated, student autonomy, elevated expectations, students as critic, using higher order thinking, knowledge, and character to critically evaluate and improve the quality of work produced by AI to solve authentic problems. Assess the process and not just the final product.